Introduction
In the realm of modern healthcare, pathology analysis plays a pivotal role in diagnosing and treating various medical conditions. Pathologists meticulously examine tissue samples to identify diseases and provide crucial insights for effective patient care. However, this traditional approach, while highly valuable, often faces challenges related to accuracy, efficiency, and workload.
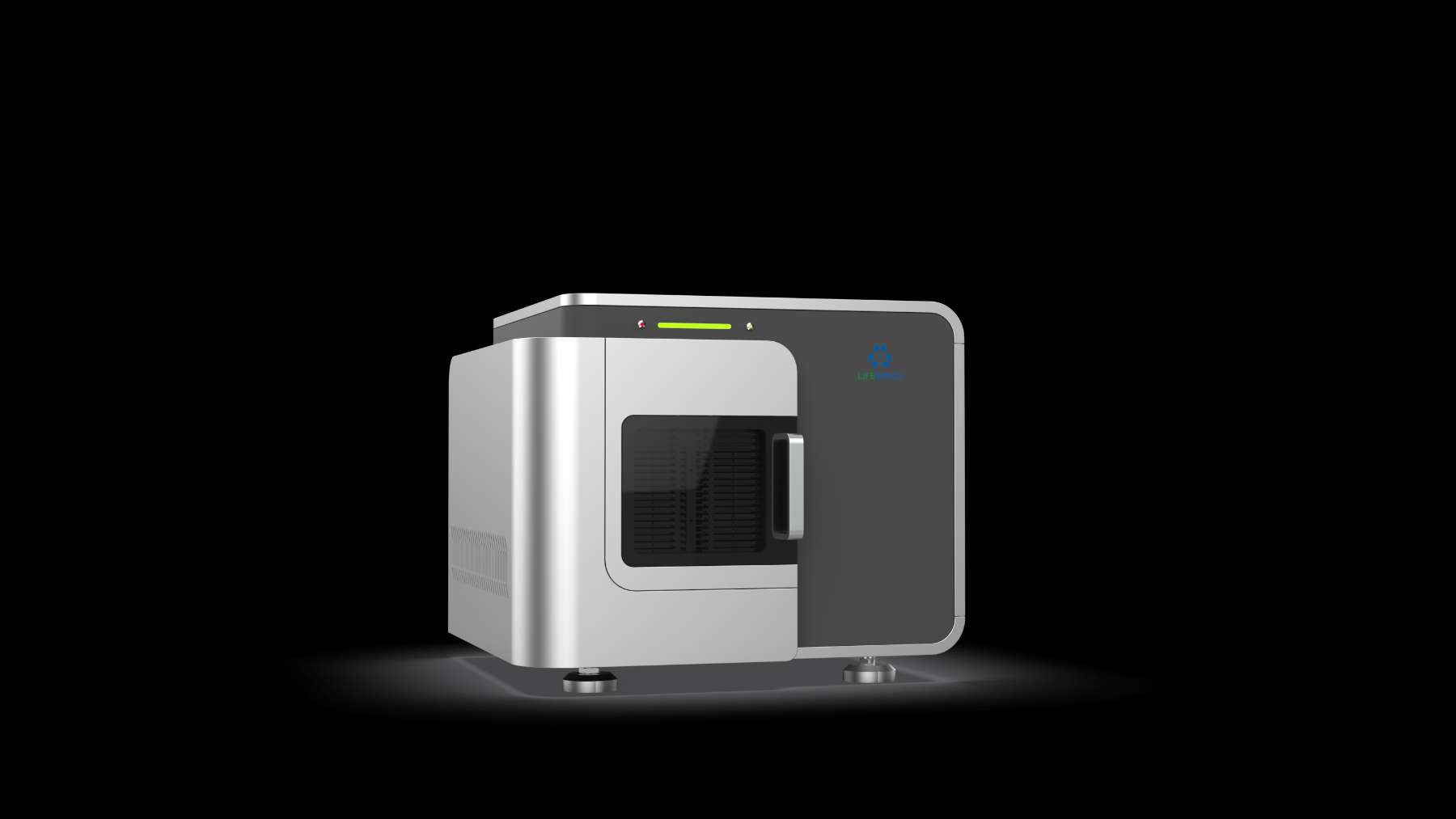
In recent years, China has taken a significant stride in addressing these challenges through the introduction of the China Automatic Pathology Analysis and Scanning System (CAPASS). CAPASS is a groundbreaking innovation that combines cutting-edge technology with medical expertise to enhance the accuracy and efficiency of pathology analysis. In this comprehensive exploration, we delve into what CAPASS is and how it works, shedding light on its transformative impact on healthcare in China and beyond.

Understanding Pathology Analysis
Before diving into CAPASS, it is essential to grasp the fundamental role that pathology analysis plays in healthcare. Pathology analysis involves the examination of tissue samples, typically obtained through biopsies or surgical procedures. This examination helps diagnose diseases, determine their stage, and guide treatment decisions.
Pathologists are highly trained medical professionals responsible for interpreting tissue samples under microscopes. While their expertise is invaluable, it is a labor-intensive process that is subject to human error and can be time-consuming.
Introduction to CAPASS
- Background and Development of CAPASS
CAPASS was developed as a response to the growing need for more efficient and accurate pathology analysis in China. The project gained momentum as part of China’s broader efforts to harness technology in healthcare.
In recent years, China has emerged as a global leader in technology adoption, and its healthcare system is no exception. The government has been actively promoting the integration of technology into healthcare services to improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden on medical professionals.
- Significance and Impact on Healthcare in China
CAPASS is a prime example of this technological transformation. It represents a significant leap forward in the field of pathology analysis. The system’s implementation has the potential to alleviate many of the challenges faced by pathologists and healthcare providers in China, such as the shortage of skilled pathologists and the need for faster diagnosis and reporting.
Key Features and Capabilities
- CAPASS boasts a range of features and capabilities that set it apart as a revolutionary tool in the realm of pathology analysis. These features include:
Scanning Technology: CAPASS utilizes state-of-the-art scanning technology, often incorporating digital microscopy, to capture high-resolution images of tissue samples. This digitization of samples allows for more efficient data acquisition and analysis.
Data Acquisition and Storage: The system is equipped to handle vast amounts of data generated from scanned tissue samples. It securely stores this data, ensuring that it is easily accessible for analysis and archiving.
Image Processing and Analysis Algorithms: CAPASS employs advanced image processing and analysis algorithms to interpret the digitized tissue samples. These algorithms are designed to identify abnormalities, classify tissue types, and flag potential areas of concern.
- Workflow of the CAPASS System
Understanding the workflow of CAPASS is crucial to comprehending how it streamlines pathology analysis. The process can be broken down into several key stages:
Sample Preparation: The journey begins with the collection of tissue samples, which are then prepared for scanning. These samples are typically mounted on glass slides, a common practice in pathology.
Scanning Process: CAPASS takes center stage during the scanning process. High-resolution images of the tissue samples are captured and stored in digital format. This step replaces the traditional method of manually examining samples under a microscope.
Data Analysis and Reporting: Once the images are captured, the system’s sophisticated algorithms come into play. They analyze the digital images, identifying cellular structures, anomalies, and other critical information. This automated analysis speeds up the diagnostic process significantly.
Integration with Healthcare Systems and Medical Professionals
CAPASS is not a standalone tool; it integrates seamlessly with existing healthcare systems and medical professionals. The digitized data and analysis results can be accessed by pathologists and other healthcare providers through secure interfaces. This integration facilitates collaboration among healthcare teams and ensures that patients receive timely and accurate diagnoses.
- Benefits of CAPASS
The adoption of CAPASS in China’s healthcare system has ushered in a range of benefits that have the potential to revolutionize pathology analysis and patient care.
- Improved Accuracy and Efficiency
One of the primary advantages of CAPASS is its ability to enhance the accuracy of pathology analysis. The system’s algorithms are designed to detect subtle abnormalities that might be missed by human pathologists. This translates to more precise diagnoses and better patient outcomes.
Additionally, CAPASS significantly improves efficiency in pathology analysis. Traditional methods of manually examining tissue samples can be time-consuming. CAPASS streamlines the process, allowing pathologists to analyze more samples in less time.
Reduction in Human Error and Subjectivity
Human error is an inherent risk in any manual process, including pathology analysis. CAPASS mitigates this risk by providing consistent, objective analysis across all samples. It reduces the potential for errors caused by fatigue, distractions, or other factors that can affect human pathologists.
Faster Turnaround Times for Pathology Reports
Timely diagnosis is critical for patient care, especially in cases of serious diseases like cancer. CAPASS expedites the diagnosis process by automating many of the time-consuming steps. This leads to faster turnaround times for pathology reports, allowing patients to start treatment sooner.
Potential for Telepathology and Remote Consultations
CAPASS has the potential to enable telepathology and remote consultations. Pathologists can access and review digital images from anywhere, making it possible to provide expertise to underserved areas or collaborate with colleagues across long distances. This is particularly valuable in regions with a shortage of pathologists.
Challenges and Limitations
While CAPASS holds great promise, it is not without its challenges and limitations.
- Cost Considerations and Infrastructure Requirements
Implementing CAPASS requires a significant financial investment. The acquisition of high-quality scanning equipment, the development of robust software, and ongoing maintenance and updates all contribute to the system’s cost. Additionally, not all healthcare facilities may have the necessary infrastructure to support CAPASS, particularly in rural or less developed areas.
- Quality Control and Calibration Issues
Maintaining the accuracy and reliability of CAPASS requires rigorous quality control measures. Calibration of scanning equipment and regular updates to the analysis algorithms are essential to ensure consistent performance. Any deviations in calibration or software updates could impact the accuracy of the system.
- Ethical and Regulatory Concerns
As with any automated system in healthcare, ethical and regulatory concerns arise. These include questions about patient data privacy, the need for human oversight, and the potential for algorithmic bias. Addressing these concerns is crucial to the responsible deployment of CAPASS.
Case Studies and Success Stories
To illustrate the real-world impact of CAPASS, let’s explore a few case studies and success stories.
- Case Study 1: Cancer Diagnosis
Imagine a patient presenting with a suspicious tissue sample. Traditionally, the sample would undergo manual examination by a pathologist, a process that could take days or even weeks. With CAPASS, the sample can be quickly digitized and analyzed by the system’s algorithms. In a matter of hours, the patient’s diagnosis is available, expediting their treatment plan and improving their chances of recovery.
- Case Study 2: Telepathology in Remote Areas
In rural areas with limited access to specialized healthcare, CAPASS can be a game-changer. A local healthcare facility can scan tissue samples and send them electronically to a pathologist in a central hub. The pathologist reviews the digital images and provides a diagnosis, all without the need for the patient to travel long distances. This not only saves time and resources but also ensures that patients in underserved areas receive the same level of expertise as those in urban centers.
Comparison with Similar Systems
While CAPASS is a remarkable achievement in the field of automated pathology analysis, it’s worth comparing it with similar systems in use worldwide.
Contrasting CAPASS with Other Automated Pathology Analysis Systems
CAPASS is not the only automated pathology analysis system in existence. Other countries and organizations have also developed similar technologies. Comparing CAPASS with these systems can provide valuable insights into its strengths and weaknesses.
Advantages and Disadvantages of CAPASS in Comparison
It’s important to consider the unique advantages and disadvantages of CAPASS in comparison to other systems. Factors such as accuracy, speed, cost, and scalability should all be evaluated in the context of the specific needs of healthcare systems.
Future Developments and Trends
The field of pathology analysis is dynamic, with continuous advancements in technology and methodology. CAPASS, as a leading innovation in this field, is likely to evolve and adapt to these changes. Here are some future developments and trends to watch for:
Emerging Technologies in Pathology Analysis
As technology continues to advance, new tools and techniques will emerge in the field of pathology analysis. CAPASS may incorporate these innovations to further enhance its capabilities.
Potential Advancements and Improvements in CAPASS
Researchers and developers will undoubtedly seek to improve CAPASS in various ways, such as refining algorithms, expanding compatibility with different types of samples, and addressing any limitations or challenges encountered during its implementation.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the China Automatic Pathology Analysis and Scanning System (CAPASS) represents a remarkable leap forward in the field of healthcare and pathology analysis. Its ability to automate and streamline the analysis process while improving accuracy and efficiency has the potential to revolutionize healthcare not only in China but also around the world.
As CAPASS continues to evolve and as similar systems are developed in other regions, the healthcare industry is poised for significant transformation. Challenges remain, such as cost considerations and ethical concerns, but with responsible implementation and ongoing refinement, CAPASS offers a promising future for patients and healthcare professionals alike.
The integration of technology into healthcare is an ongoing journey, and CAPASS is a shining example of the possibilities that lie ahead. With a commitment to quality, ethical practices, and patient-centered care, CAPASS is a beacon of hope for a healthier, more efficient, and more accessible healthcare future.